Senegalese National Gendarmerie
|
1960 Ministry of attachment: Ministère des forces armées Workforce: 8 500 General manager: Général de division Meïssa NIANG Address: 14, rue Émile ZOLA Tél.: 00221 77 644 76 18 Fax: 00221 33 823 42 06 Email: gbmeissa@yahoo.fr Website: www.gendarmerie.sn 
|
History
Before the independence, the presence of the French gendarmes dates back to 1843. In 1854, a "gendarmes on foot’s detachment" is created by the imperial decree of September 30th. From 1854 till 1915, the detachment undergoes numerous workforce changes and its existence is questioned several times. Suppressed from 1890 till 1899, it knows from 1915 a progressive phase of increase. Lieutenant Gaston Merhle, placed at the head of the detachment from 1921 till 1941, encourages its development. He spreads out the competence of the institution, increases its brigades network, which, from Senegal, gradually extends beyond the French Sudan (current Mali) and the Guinea. In 1928, he creates the Red Guard, prestigious elite unit still in service. From 1945, the detachment, which is transformed into company by the decree of August 23rd, 1949, knows a period of fast expansion. In 1954, the workforce is 40 officers, 589 non-commissioned officers and 1 443 auxiliaries. In 1957, the Senegal Gendarmerie Group is established by the ministerial decision of November 27th. In 1958, the first Senegalese pupils-gendarmes are recruited. In January 1960, the Senegal Gendarmerie squad includes a general staff, 2 mobile squadrons (one of them "mounted") and 5 territorial companies.
On June 20th, 1960, Senegal reaches the independence within the federation of Mali, before seceding on August 20th with the support of the Senegalese gendarmes. In 1962, the first director is captain Ameth Fall. In 1963, the decree N° 63-294 of May 11th organizes the Senegalese National Gendarmerie that is an integral part of Senegalese armed forces. In May 1964, the decree N° 64-347 establishes an assistant director. In October 1965, the decree N° 65-965 organizes the Gendarmerie General Inspectorate and the Senegalese Republican Guard. In 1968, the decree N° 68-929 of August 28th reorganizing the Senegalese Gendarmerie reaffirms its membership in armed forces. The Senegalese National Gendarmerie is managed by a High Commander, assisted by a Gendarmerie Forces Commander (Brigadier-general Jean Alfred Diallo is appointed Gendarmerie High Commander and Major Wally Faye, Gendarmerie Force Commander).

From 1972, the Gendarmerie High Commander and Military Justice Director depends directly on the ministry of Armed forces. He has the rank and the prerogatives of the Army General Joint Staff Chief. In 1974, the decree N° 74-751 of June 13th regulates the employment and the service of the Gendarmerie. In July 1974, the decree N° 74-714 concerning the organization of the Senegalese National Gendarmerie restores a Senegalese gendarmerie Direction. In July 1976, the Senegalese National Gendarmerie missions increasing over from day to day, an Intervention Gendarmerie Corps is created. The decree N° 76-778 of July 22nd, 1976 is fixing up its organization and its employment. In August 1977 the Senegalese National Gendarmerie Intervention Force (NGIF) is set up.
In December 1981, Gendarmerie High Commander title reappears. In August 1984, the Law N° 84-62 of January 16th reorganizes the Senegalese armed forces. The evolution of the structures at the level of the latter, leads to the creation of two major subdivisions of this arm, the anti-riot police and the territorial gendarmerie. In 1991, the decree N° 91-803 of August 23rd organizes the Senegalese National Gendarmerie High command and fixes the authorities of command’s attributions. The Territorial Gendarmerie Corps see the lights of day. In 2000, the corps counts 4 833 men. In 2006, the decree N° 2006-515 of June 9th opens the non-commissioned officers recruitment to the women. In 2007, the decree N° 2007-93 of January 29th creates the National Gendarmerie Officer’s School (NGOS) in Dakar. In 2008, the decree N° 2008-1012 of August 18th fixes the Senegalese gendarmerie personnel particular status.
Organization
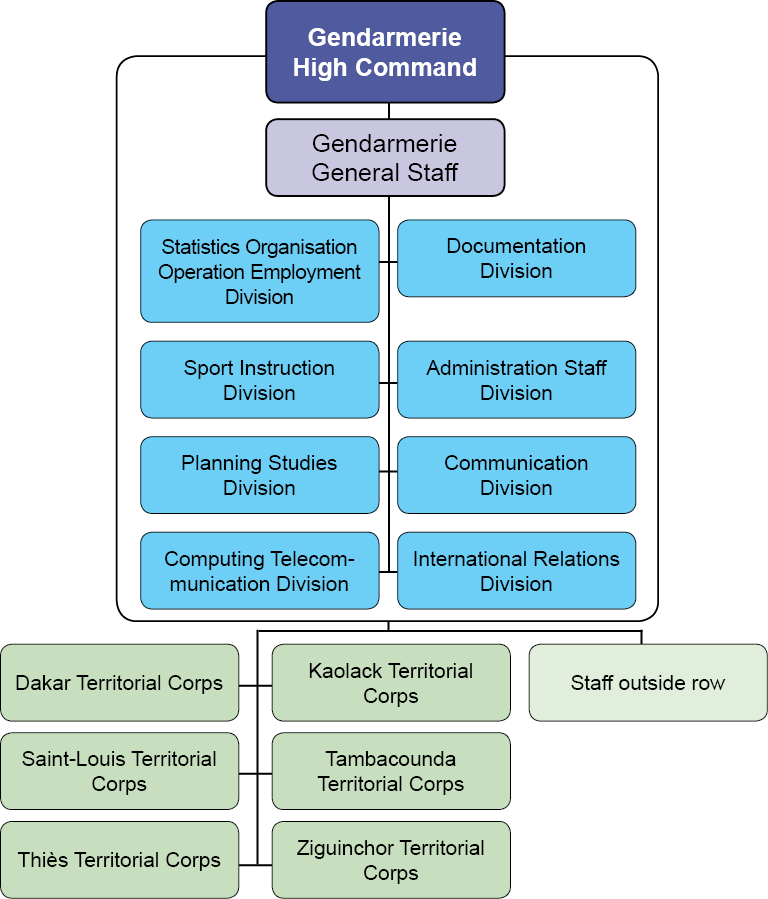
Central Organization
The decree N° 2005-123 of February 17th, 2005 fixes the organization of the National Gendarmerie High Command. For the exercise of his function, the National Gendarmerie High Commander, assisted by a second-in-command High-Commander, has at his disposal:
• a cabinet;
• the Gendarmerie high command general staff;
• the Commands of the territorial gendarmerie, the anti-riot police/"Mobile Gendarmerie" and the Gendarmerie schools;
• specialized services;
• technical inspectors.
The gendarmerie general staff, placed under the National Gendarmerie High Commander’s authority, is managed by a general officer or a senior officer: the chief of staff appointed by decree. It includes in particular:
• the Statistics Organisation Operation Employment Division (SOOE);
• the Documentation Division (DD);
• the Sport Instruction Division (SID);
• the Administration Staff Division (ASD);
• the Planning Studies Division (PSD);
• the Communication Division (COM DIV);
• the Computing Telecommunication Division (CTD);
• the International Relation Division Told international (IRD).
Every division is managed by a senior officer appointed by an Armed Forces Minister’s order and having a commanding officer’s rank and advantages.
The Chief of staff has direct authority on the divisions, and exercises with regard to them the territorial or "Mobile gendarmerie" Commander’s same responsibilities and prerogatives he has the row and the advantages.
Territorial organization
• 6 territorial corps of gendarmes (Dakar, Kaolack, Saint-Louis, Tambacounda, Thiès, and Ziguinchor).
• An outside row Legion; in charge of the staff administration in OPEX and in service in forces staff and service.
• 17 Companies.
• 120 Territorial Brigades.

Specialized Training
• 3 "Mobile" corps of gendarmes all implanted in Dakar: the Intervention Corps of gendarmes (ICG), the Protection and Security Corps of Gendarmes (PSCG) and the Presidential Guard Corps of Gendarmes (PGCG).
• Specialized units: Researches (Criminal investigations) Section (RS), Environment Section (ES) created in 2003, a National Gendarmerie Intervention Group (NGIG), and a Dog Group.
Missions
Covering nearly 80% of the national territory, the Senegalese Gendarmerie performs the missions defined by the decree N° 74-751 of June 13th, 1974:
• of Criminal Investigation Department;
• of administrative police (traffic police, trading police, mobile professions police, entertainments beverages, public health, aviation, river public domain, railroads, coastal shipping police, fishing and hunting);
• of military police.

 Staff
Staff
The Senegalese National Gendarmerie counts 8 500 servicemen among whom 412 officers, 6 130 non-commissioned officers and 1 958 auxiliary gendarmes. The Gendarmerie staffs are mainly of the career soldier category. They belong to two different corps: the officers’ corps (From the officer cadet’s rank to the general’s rank) and the non-commissioned officers’ corps (From the gendarme’s rank to the major-chief warrant officers).
The Senegalese National Gendarmerie also includes the category of Gendarmerie pupils-officers, pupils-gendarmes and auxiliary gendarmes. The latter are servicemen of the contingent given to the gendarmerie in order to serve during the legal duration of the military service, which is of two years in Senegal. Members of the armies, their employments are subject to a ministerial instruction. The admission in the Gendarmerie officers and non-commissioned officers’ corps is the verdict of the training received in the gendarmerie schools.
Training institutions
• A Gendarmerie officers’ school.
• A non-commissioned officers school.
• Specialized training centres (the auxiliary gendarmes’ instruction centre, the anti-riot police improvement centre, the Criminal Investigation Department national centre).
Main equipment
• Armament: M16 rifles and Taurus PA (some Tikka and FRF1).
• Light Vehicles: Foton pick-up (China), Panhard AML 60 and 90, Cruisair cars (France), miscellaneous command and liaison type Toyota Fortuner or Prado and Suzuki swift vehicles.
• Transport and Fight Armoured Vehicles: 12 VBRG.
• Air means: 3 reconnaissance planes acquired in 2014 (G1 SPYL - France).

Cooperation
The Senegalese National Gendarmerie maintains historical relations with the French Gendarmerie but it also develops a cooperation with, in particular, the Spanish Civil Guard, the Italian Carabineers corps, the American FBI, as well as with the African sisters gendarmeries as the Moroccan royal Gendarmerie and all those who are members of the African Gendarmerie Organization (AGO).
Senegal is committed since its independence in Peacekeeping operations. Its gendarmerie is present on several theatres of operations, in particular in Haiti, in Congo Democratic Republic, in the Darfur and in Mali.

© The iconography was provided by the concerned gendarmeries